Introduction
In this chapter, “Microorganisms: Friend and Foe,”JKBOSE class 8th science chapter 1, we will explore what microorganisms are and the various ways they can be both beneficial and harmful to us. Microorganisms are tiny organisms that can only be seen with the help of a microscope. They play essential roles in our lives, contributing to processes like digestion, fermentation, and nutrient cycling. However, some microorganisms can also cause diseases and infections. Understanding these dual roles is crucial for appreciating the impact of microorganisms on health and the environment.
Keywords
Algae
Algae are simple, plant-like organisms that usually live in water. They can make their own food through photosynthesis and range in size from tiny, single-celled forms to large seaweeds.
Antibodies
Antibodies are proteins produced by the immune system to recognize and fight harmful invaders like bacteria and viruses. They attach to these invaders to help the body neutralize or destroy them, protecting us from infections.
Bacteria
Bacteria are single-celled microorganisms found almost everywhere, from soil to the human body. Some bacteria are helpful, while others can cause diseases. They come in various shapes, like rods, spheres, or spirals.
carrier
A carrier is an organism, usually a person or animal, that carries and spreads disease-causing microorganisms without showing any symptoms of the illness. Carriers can transmit the disease to others, even though they appear healthy.
Communicable diseases
Communicable diseases are illnesses that can spread from one person to another through direct contact, air, water, or infected surfaces. Examples include the flu, measles, and tuberculosis. These diseases are caused by microorganisms like bacteria, viruses, or fungi.
Fermentation
Fermentation is when microorganisms break down sugars into alcohol or acids, used to make bread, yogurt, and beer.
Fungi
Fungi are eukaryotic organisms that include molds, yeasts, and mushrooms. They help decompose organic matter and can be beneficial in food production or harmful by causing diseases in plants and animals.
Lactobacillus
Lactobacillus is a type of bacteria that helps convert milk into curd or yogurt. It is also found in the human gut and supports digestion and overall health.
Microorganisms
Microorganisms are tiny living things that can’t be seen without a microscope. They include bacteria, viruses, fungi, and more.
Nitrogen fixation
Nitrogen fixation is the process of converting atmospheric nitrogen (N₂) into ammonia (NH₃) or other usable forms for plants. This is primarily done by bacteria, such as
Nitrogen cycle
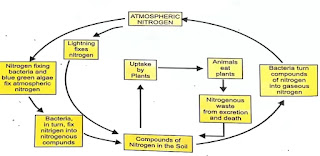
The nitrogen cycle describes how nitrogen moves through the atmosphere, soil, and living organisms. Atmospheric nitrogen (N₂) is fixed by certain bacteria and blue-green algae into usable nitrogen compounds that plants can absorb through their roots. Plants use these compounds to create proteins and other essential substances, which animals obtain by eating plants. When plants and animals die, bacteria and fungi decompose their nitrogenous wastes, converting them into usable compounds for plants again. Some bacteria also convert these compounds back into nitrogen gas, returning it to the atmosphere, thus maintaining a balanced nitrogen level.
Pasteurization
Pasteurization is a heat treatment process that kills harmful microorganisms in food and beverages, like milk and juice, to make them safe to consume and extend shelf life. It involves heating the product to a specific temperature for a set time and then cooling it quickly.
Pathogens
Pathogens are harmful microorganisms, such as bacteria, viruses, fungi, and protozoa, that can cause diseases in humans, animals, and plants. They can enter the body through various means, including air, water, contaminated food, or direct contact with infected individuals.
Preservation
Preservation is the process of protecting food and perishable items from spoilage. Techniques include:
1. Refrigeration: Slowing bacteria growth with low temperatures.
2. Canning: Sealing food in airtight containers.
3. Freezing: Stopping bacterial growth with very low temperatures.
4. Drying: Removing moisture to inhibit spoilage.
5. Fermentation: Using beneficial microorganisms to prevent spoilage.
These methods help extend shelf life and maintain quality.
Protozoa are single-celled eukaryotic microorganisms found in various environments, including water and soil. They can be free-living or parasitic and play roles in ecosystems, such as decomposition. Some protozoa cause diseases in humans and animals, like malaria and amoebic dysentery.
Rhizobium
Rhizobium is a bacteria that lives in the root nodules of leguminous plants, such as beans and peas. It fixes atmospheric nitrogen into a usable form for the plants, enriching the soil and benefiting both the bacteria and the plants.
vaccine
A vaccine is a preparation that stimulates the immune system to recognize and combat specific pathogens, such as viruses or bacteria. It helps protect individuals from diseases by building immunity without causing the illness.
virus
A virus is a tiny infectious agent that can only replicate inside living cells. It consists of genetic material surrounded by a protein coat and causes diseases like the flu and COVID-19. Viruses are not considered living organisms.
Yeast
Yeast is a single-celled fungus used in baking and brewing. It ferments sugars to produce alcohol and carbon dioxide, making it essential for bread and drinks.
1. Fill in the blanks.
(a) Microorganisms can be seen with the help of a Microscope
(b) Blue-green algae fix Nitrogen directly from the air to enhance the fertility of soil.
(c) Alcohol is produced with the help of Yeast
(d) Cholera is caused by bacteria
2. Tick the correct answer
a. Yeast is used in the production of
b. The following is an antibiotic:
c. Carrier of malaria-causing protozoan is:
d. The most common carrier of communicable diseases is
e. The bread or idli dough rises because of:
f. The process of conversion of sugar into alcohol is called
Column I Column II
| Column I | Column II |
| (i) Bacteria | (a) Fixing Nitrogen |
| (ii) Rhizobium | (b) Setting of curd |
| (iii) Lactobacillus | (c) Baking of bread |
| (iv) Yeast | (d) causing of Malaria |
| (v) A Protozoan | (e) Causing of Cholera |
| (vi) A Virus | (f) Causing of AIDS |
| (g) Production of antibodies |
| Column I | Column II |
| (i) Bacteria | (e) Causing of Cholera |
| (ii) Rhizobium | (a) Fixing Nitrogen |
| (iii) Lactobacillus | (b) Setting of curd |
| (iv) Yeast | (c) Baking of bread |
| (v) A Protozoan | (d) causing of Malaria |
| (vi) A Virus | (f) Causing of AIDS |
Question 4.
Can microorganisms be seen with the naked eye? If not, how can they be seen?
Answer:
We can’t see microorganisms with our eyes because they are so tiny. Some, like the fungus that grows on bread, can be viewed with a magnifying glass. But many can only be seen using a microscope.
Question 5.
What are the major groups of microorganisms?
Answer:
Microorganisms are grouped into four main categories based on their size. These are:
(a) Bacteria
(b) Fungi
(c) Protozoa
(d) Certain types of algae
Question 6.
Name the microorganisms which can fix atmospheric nitrogen in the soil.
Answer:
Microorganisms that can fix atmospheric nitrogen in the soil include bacteria such as Rhizobium, Azotobacter, and Cyanobacteria (also known as blue-green algae).
Question 7.
Write 10 lines on the usefulness of microorganisms in our lives.
Answer:
Microorganisms are beneficial in many ways, such as:
- Yeast is used in producing alcohol, wine, and baked goods.
- Some microorganisms are used to produce antibiotics.
- Lactobacillus bacteria turn milk into curd.
- Certain bacteria help fix nitrogen, improving soil fertility.
- Acetobacter aceti produces acetic acid from alcohol.
- Microorganisms break down waste into manure, acting as natural cleaners.
- Vaccines are made using dead or weakened microbes.
- Bacteria help in making cheese.
- Microorganisms like algae, yeast, fungi, and bacteria can be used as protein-rich food substitutes.
- Some microorganisms are used as probiotics, believed to support health when consumed.
Question 8.
Write a short paragraph on the harms caused by microorganisms.
Answer:
Microorganisms can be harmful in many ways. For instance, pathogens (harmful microorganisms) cause diseases in humans, animals, and plants. These germs can enter the body through air, water, contaminated food, or contact with infected individuals, either directly or indirectly. Here are some examples:
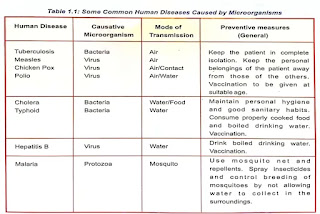
– Viruses cause common illnesses like colds, flu, polio, chickenpox, and foot-and-mouth disease in cattle.
– Bacteria are responsible for diseases such as typhoid, tuberculosis (TB), and anthrax (which affects both humans and cattle).
– Protozoa cause diseases like dysentery and malaria.
– Fungi cause infections like ringworm.
Microorganisms also harm plants by reducing crop yields:
– Citrus canker, a bacterial disease, affects citrus trees and spreads through the air.
– Bhendi yellow vein mosaic disease is a viral infection in ladyfinger plants, spread by insects.
– Rust of wheat is a fungal disease spread by air.
In addition, some microorganisms growing on food release toxins that make it unsafe to eat, leading to food poisoning, which can cause serious illness or even death.
Question 9.
What are antibiotics? What precautions must be taken while taking antibiotics?
Answer:
Antibiotics are medicines that either kill or stop the growth of harmful microbes. They are made by growing specific microorganisms and are used to treat various diseases.
Precautions:
It’s important to only take antibiotics as prescribed by a doctor. Completing the full course is necessary to ensure the medicine works effectively. Taking antibiotics without need can harm beneficial bacteria in the body. However, antibiotics do not work against illnesses like colds and flu, which are caused by viruses.